Practical
Task 1 - JavaScript Guessing Game
Set Up
Within a new folder create the following files:
- js/main.js
- index.html
Within
main.jscreate a function calledmain, for now it will just have one line of code in italert('working')Within
index.htmls body tag, add a inline load even that calls the functionmain.<body onload="main()">
Main Task
The aim of the task this week is to create a number guessing game. Your program will generate a number between a user defined range. The user will then make guesses with the aim of finding that number. Feedback will be given on if the guess is:
- Smaller than the number
- Larger than the number
- An exact match!
- Add the following elements to
index.htmland give themid's where appropriate:
- An input and label for the guess
- A
<button>Click Me </button>that will be pressed after the guess - A paragraph to hold the result
At the top of your javascript file create vars to hold the following values:
- random_number
- number_of_guesses
Math.round(Math.random() * (20 - 10) + 10);generates a random number between 20 and 10. The formula looks like thisMath.round(Math.random() * (max - min) + min);. Create a functiongetRandomArbitrary(min, max)which returns a random number between any given range.Set
random_numberequal to a random number by using the above function. This should be done inmain()which is called when the page has loadedUsing external javescript add a click event to the button that runs a guess function.
Write the guess function, it should grab the the user input and run some comparisons and adjust the
inner_htmlvalue of your paragraph to display the information based on the guess.Advanced set up a variable called
var number_of_guesses = 10, decrement this variable on each guess. If the user runs out of guesses it's game over. The inputs should then be hidden.
Task 2 - Solent Stores
Solent Stores - Shopping cart exercise
The purpose of this exercise is to extend/improve/finish the solent stores exercise from last week. Once this is done, please work on your assignment
1 Setup
Download the project source file from here. Open up index.html in your browser, you should be presented with the following website:
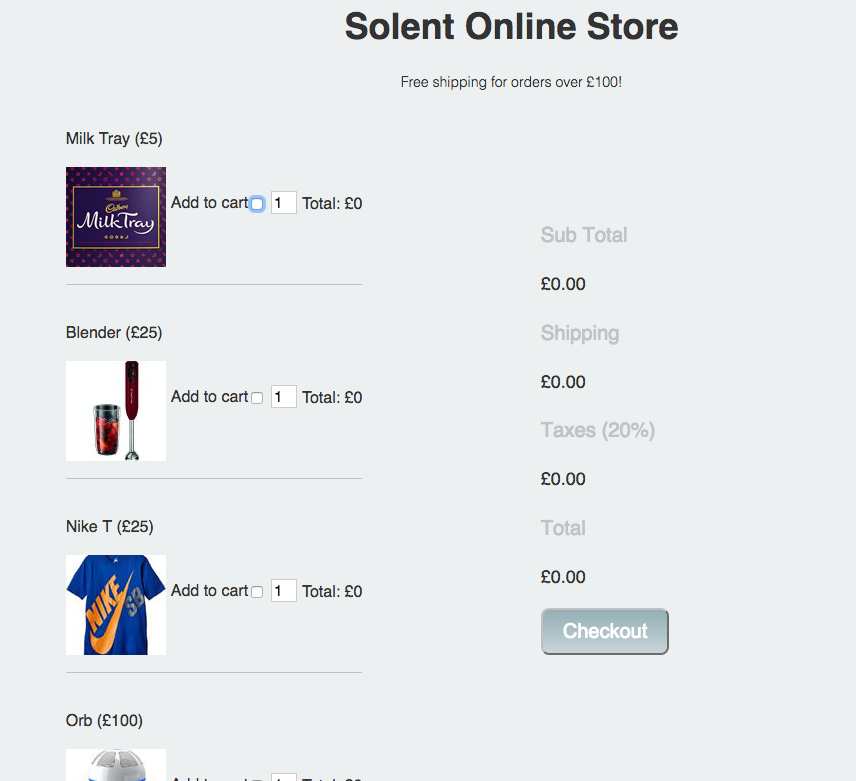
2 Add a data attribute to hold the price of each product
If you take a look at your source code for index.html you'll see that each product has a checkbox for the add to cart functionality. Heres the one for our blender:
<input type="checkbox" name="product" value="blender">
At the a data attribute to hold the of each item. For example, our blender input would become:
<input type="checkbox" name="product" data-price = "25" value="blender">
3 Our first bit of javaScript
Within index.html, notice how we've included an external javaScript file and also added a onLoad event that calls a main() function.
- Open up
script/main.js - Within
main.jsadd an event listener that fires theformChangedFunction - Check that the message is output to the console when the form changes
4 Working out the main totals and shipping costs
- Within
main.jsformChangeFunctioncreate the following variables:
var form = document.getElementById("productForm");
var subTotal = 0;
var shipping = 0;
var taxes = 0;
var total = 0;
- Next, within
formChangedFunctionCreate a for loop that loops through theproductcheck list, if a product has been checked you should cast thepriceto a number and add it to the subtotal. This is very similar to our the example in the notes.
numberTotal = parseInt(form.product[i].dataset.price);
subTotal = subTotal + numberTotal;
how to access the price from within the loop
Note, this is very similar to the in class example.
- After the loop, check to see if the
subTotalis less than £100. If this is the case, setshipping = £10 - Set the variable
taxes = 20% of subTotal - Set the variable
total = subTotal + taxes + shipping - Set the inner HTML of each section in the summary table = to your new variable values:
document.getElementById("sub-total").innerHTML = "£" + subTotal;
document.getElementById("shipping").innerHTML = "£" + shipping;
document.getElementById("taxes").innerHTML = "£" + taxes;
document.getElementById("total").innerHTML = "£" + total;
5 Product totals and multiple items
Implement the functionality to allow the amount of each product to be increased. The total for each product should be displayed. This is tricky, but let's take the blender as an example and consider its related elements:
<input data-price="25" type="checkbox" name="product" value="blender">
<input type="number" value="1" name="blender-quantity">
<p>Total: <span id="blender-total"> £0 </span> </p>
This naming convention is consistent for all the products, your solution will take advantage of this.
6 Add real time form validation
The quantity box should go red if a number is entered below 0 or above 100.
7 Add a order summary
Above the checkout button add a order summary. This should be a list of items that have been selected in human readable form. It should be updated in real-time. To achieve this you'll need to add a desc attribute to each of you of your check boxes:
```<input type="checkbox" name="product" data-desc="Milk Tray" value="mt">```